The Evolution of PC Storage – From HDD to NVMe and Beyond

A deep dive into the evolution of PC storage technology, from traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) to modern NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) SSDs, and what the future holds for data storage in PCs.
6.1 The Shift from HDD to SSD
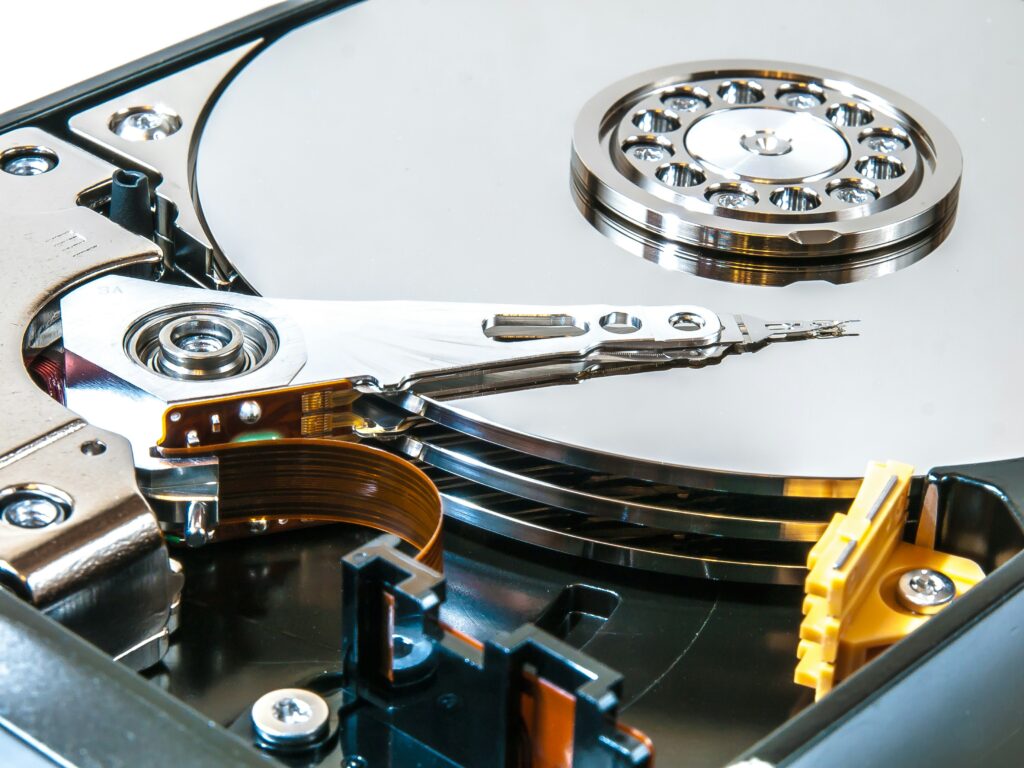
For decades, hard disk drives (HDDs) were the primary storage solution for PCs, offering large storage capacities at relatively low cost. However, as technology advanced, solid-state drives (SSDs) became the preferred option due to their faster speeds, improved reliability, and energy efficiency. SSDs use flash memory, which allows for much quicker read and write speeds compared to the mechanical nature of HDDs.
HDDs (Legacy Storage): HDDs still play a role in PCs, particularly for users who need large storage capacities without the need for high-speed data transfer. HDDs are often used in servers, backup solutions, and budget PCs.
SSDs (Faster, More Reliable Storage): SSDs offer drastically faster data transfer rates, with boot times and file transfers taking mere seconds compared to HDDs. They are also more durable, as they contain no moving parts, reducing the likelihood of data loss due to mechanical failure.
6.2 The Emergence of NVMe Technology
What is NVMe? NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a storage interface designed specifically for SSDs, enabling faster communication between the storage device and the PC’s processor. NVMe drives use PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) lanes, which offer significantly more bandwidth than the SATA interface used by older SSDs.
Performance Gains: NVMe SSDs provide read and write speeds that are up to six times faster than SATA-based SSDs. This makes them ideal for high-performance computing tasks such as gaming, video editing, and data analysis, where speed is critical.
M.2 and U.2 Form Factors: NVMe SSDs come in different form factors, with M.2 being the most common for consumer PCs due to its compact size. U.2 form factors are typically used in enterprise settings where large storage capacities are required.

6.3 The Future of PC Storage – What Comes Next?
Optane Memory: Intel’s Optane memory technology offers a hybrid solution that combines the speed of RAM with the storage capacity of an SSD. Optane aims to reduce latency and provide near-instantaneous access to data, making it an attractive option for future PCs that require even faster storage solutions.
Holographic Storage: Although still in development, holographic storage holds promise for the future. This technology uses light to store data in three dimensions, potentially offering storage capacities far beyond what is currently achievable with SSDs or even traditional HDDs.
DNA Storage: Another frontier in data storage is DNA-based storage. Researchers are working on using synthetic DNA to store massive amounts of data in a very small space. Although it’s still in the experimental phase, DNA storage could revolutionize how data is stored and accessed in the future, with near-limitless storage potential.
6.4 Challenges and Future Outlook
While NVMe SSDs have become the gold standard in PC storage, there are still challenges to overcome. Price remains a barrier for some users, as NVMe drives are typically more expensive than traditional HDDs or SATA SSDs. However, as technology advances and production costs decrease, NVMe and future storage solutions like Optane and holographic drives are expected to become more accessible to everyday consumers.